Understanding UK Nominal Voltage: A Comprehensive Guide
When it comes to electrical systems, understanding UK nominal voltage is crucial for ensuring safety and efficiency. Whether you're a homeowner, an electrician, or just someone curious about how electricity works, this topic deserves attention. The UK nominal voltage plays a significant role in powering homes, businesses, and industries across the nation. So, let's dive right in and explore what it means and why it matters.
In today's world, electricity powers almost every aspect of our lives. From charging your smartphone to running heavy machinery, voltage is the backbone of modern technology. But what exactly is nominal voltage, and why does the UK have specific standards? We'll break it down step by step so that even if you're not an expert, you'll walk away with valuable insights.
Before we get too technical, let's address the basics. The UK nominal voltage is designed to provide a stable and reliable power supply to meet the demands of various devices and appliances. It's like the fuel that keeps everything running smoothly. As we explore further, you'll discover how this system works and how it impacts your daily life. Ready? Let's go!
Read also:Tamara Smart Rising Star In The Entertainment World
What is UK Nominal Voltage?
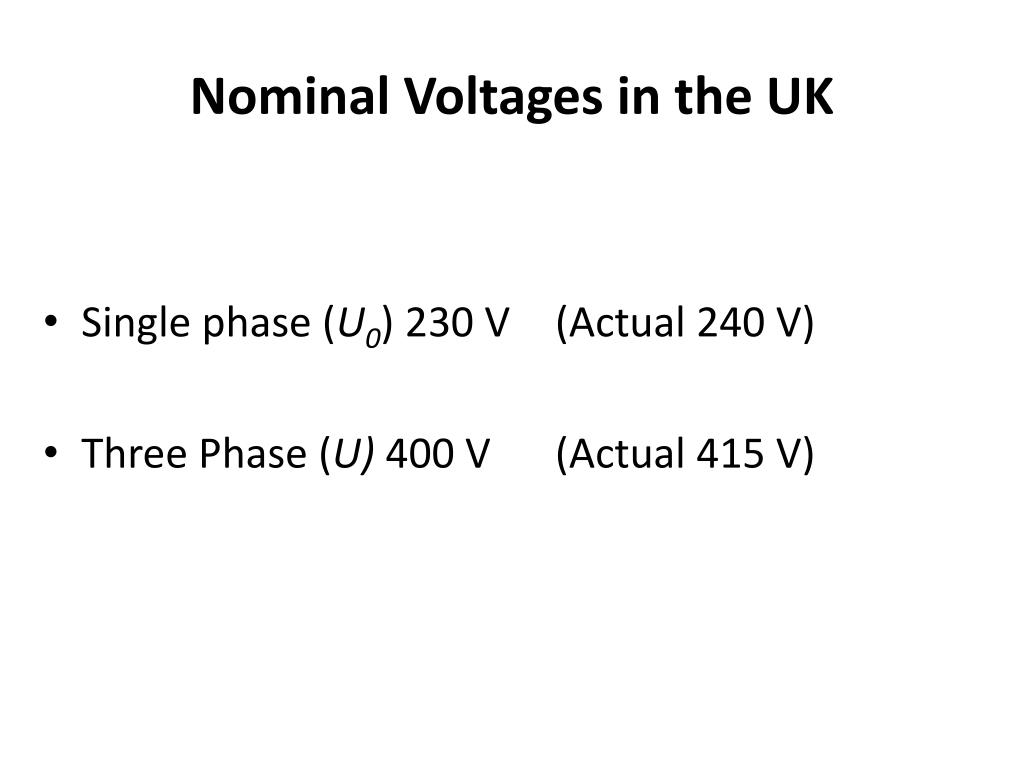
Alright, let's start with the foundation. UK nominal voltage refers to the standard voltage level used in the United Kingdom for electrical distribution. This voltage is designed to ensure consistent power delivery across different regions. Currently, the UK operates on a nominal voltage of 230 volts, which aligns with European standards.
Now, you might be wondering, "Why 230 volts?" Well, this value was chosen to balance efficiency and safety. Higher voltages reduce energy loss during transmission, while lower voltages minimize risks associated with electrical hazards. The 230-volt standard strikes the perfect compromise.
Let's break it down further:
- Nominal voltage: 230V
- Tolerance range: ±10%
- Frequency: 50Hz
These specifications ensure that devices and appliances operate efficiently and safely within the UK's electrical grid.
History of UK Voltage Standards
From 240V to 230V
Back in the day, the UK used a nominal voltage of 240 volts. However, things changed in the late 1980s when Europe adopted a harmonized voltage standard. To align with other countries, the UK shifted to 230 volts. This transition wasn't just about numbers; it was about promoting interoperability and consistency across Europe.
During the transition, many devices were designed to accommodate both 240V and 230V. This dual compatibility ensured a smooth shift without disrupting existing equipment. Over time, manufacturers began producing appliances specifically for the new standard, making the switch seamless for consumers.
Read also:Cristy Lee The Rising Star Whos Taking The World By Storm
Why Does Nominal Voltage Matter?
Nominal voltage isn't just a number; it's a critical factor in how electricity is distributed and consumed. Here's why it matters:
- Efficiency: Proper voltage levels ensure that devices operate at their optimal performance.
- Safety: Staying within the tolerance range minimizes the risk of electrical faults and accidents.
- Compatibility: Standardized voltage allows devices from different manufacturers to work together seamlessly.
Think of it like driving a car. If the fuel isn't the right type or grade, your engine won't perform as expected. Similarly, if the voltage isn't within the specified range, your appliances might underperform or even get damaged.
How is Voltage Regulated in the UK?
The regulation of voltage in the UK is a well-organized process. National Grid, along with regional distribution companies, ensures that voltage levels remain within the ±10% tolerance range. This involves constant monitoring and adjustments to account for fluctuations in demand.
Here's how it works:
- Generation: Power plants produce electricity at high voltages for efficient transmission.
- Transmission: Electricity is transported through high-voltage lines to substations.
- Distribution: Substations step down the voltage to 230V for residential and commercial use.
By maintaining this structured approach, the UK ensures a stable and reliable power supply for everyone.
Impact of Voltage Fluctuations
Understanding Voltage Drops and Spikes
Even with strict regulations, voltage fluctuations can occur. These variations, known as voltage drops or spikes, can impact your devices. For instance, a sudden spike might overload your appliances, while a drop could cause them to underperform.
Here are some common causes of voltage fluctuations:
- High demand during peak hours
- Weather conditions affecting power lines
- Equipment malfunctions or faults
To protect your devices, consider using surge protectors or voltage stabilizers. These tools help mitigate the effects of fluctuations and keep your equipment safe.
Common Misconceptions About UK Nominal Voltage
There are a few myths floating around when it comes to UK nominal voltage. Let's debunk them:
- Myth 1: Higher voltage always means better performance. Not true! Excessive voltage can damage your devices.
- Myth 2: Voltage fluctuations are rare. Wrong! They happen more often than you think, especially during extreme weather.
- Myth 3: All devices are compatible with 230V. False! Some imported appliances may require voltage converters.
By understanding these misconceptions, you can make more informed decisions about your electrical setup.
Practical Tips for Managing Voltage
Now that you know the importance of nominal voltage, here are some practical tips to help you manage it effectively:
- Regularly check your electrical connections for signs of wear or damage.
- Invest in quality surge protectors to safeguard your valuable electronics.
- Consider upgrading your wiring if your home is old and hasn't been updated recently.
These simple steps can go a long way in ensuring the longevity and safety of your electrical systems.
Future Trends in Voltage Standards
Smart Grid Technology
As technology advances, so do voltage standards. The UK is exploring smart grid technology to enhance power distribution. These grids use advanced sensors and automation to monitor and adjust voltage levels in real-time. This innovation promises improved efficiency and reduced energy waste.
Additionally, renewable energy sources like solar and wind are becoming more integrated into the grid. This shift requires flexible voltage management systems to accommodate varying power outputs. The future of electricity is exciting, and the UK is at the forefront of these developments.
Conclusion: Embrace the Power of Knowledge
In summary, understanding UK nominal voltage is essential for anyone dealing with electricity. From its history and regulation to its impact on daily life, this topic touches every aspect of modern living. By staying informed and taking proactive steps, you can ensure a safe and efficient electrical environment for yourself and your family.
So, what's next? Share this article with friends and family who might benefit from this knowledge. Leave a comment below if you have questions or insights to add. Together, let's keep the conversation about electricity flowing!
Table of Contents
- What is UK Nominal Voltage?
- History of UK Voltage Standards
- Why Does Nominal Voltage Matter?
- How is Voltage Regulated in the UK?
- Impact of Voltage Fluctuations
- Common Misconceptions About UK Nominal Voltage
- Practical Tips for Managing Voltage
- Future Trends in Voltage Standards
- Conclusion